Sports injuries are the injuries that most commonly occur during sports and exercises. These injuries may result from accidents, poor training practices, and use of improper protective gear, lack of conditioning, and insufficient warm up and stretching. The sports injuries may be either acute (sprains, fractures, tears) or chronic (tendinitis, overuse injury) injuries.
Some of the common knee injuries experienced by sports individuals include:
- Meniscal tear: The two wedge-shape cartilage pieces present between the thighbone and the shinbone are called meniscus. They stabilize the knee joint and act as “shock absorbers. Meniscal tear is the commonest knee injury in athletes, especially those involved in contact sports. A suddenly bend or twist in your knee cause the meniscus to tear. This is a traumatic meniscus tear. Torn meniscus causes pain, swelling, stiffness, catching or locking sensation in your knee making you unable to move your knee through its complete range of motion.
- Patellar Instability: Patellar (knee cap) instability results from one or more dislocations or partial dislocations (subluxations). Patella is the small piece of bone in front of the knee that slides up and down the femoral groove (groove in the femur bone) during bending and stretching movements. The ligaments on the inner and outer sides of patella hold it in the femoral groove and avoid dislocation of patella from the groove. Any damage to these ligaments may cause patella to slip out of the groove. Once damaged, these soft structures are unable to keep the patella (knee cap) in position. Repeated subluxation or dislocation makes the knee unstable and the condition is called as knee instability.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), one of four major ligaments of the knee is situated at the back of the knee. It connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). The PCL limits the backward motion of the shinbone.PCL injuries are very rare and are difficult to detect than other knee ligament injuries.
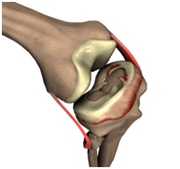
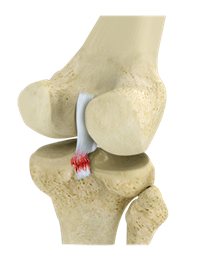
The PCL is usually injured by a direct impact, such as in an automobile accident when the bent knee forcefully strikes the dashboard. In sports, it can occur when an athlete falls to the ground with a bent knee. Twisting injury or overextending the knee can cause the PCL to tear. Patients with PCL injuries usually experience knee pain and swelling immediately after the injury. There may also be instability in the knee joint, knee stiffness that causes limping, and difficulty in walking.
If you do not have any symptoms mentioned above, you can adopt self –care treatment at home. You should follow the RICE treatment—Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation immediately after injury to relieve pain and inflammation.
Your doctor may recommend other treatments to help your injury heal. These include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: These drugs reduce swelling and pain.
- Immobilization: Immobilization is minimizing the movement of injured area to prevent further damage. It also reduces pain, swelling, and muscle spasm.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation involves exercises that get the injured area back to normal condition. Exercises start with gentle range-of-motion exercises followed by stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Other Therapies: Other common therapies that help in the healing of sports injuries include mild electrical currents (electrostimulation), cold packs or cryotherapy, heat packs or thermotherapy, high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound), massage and platelet rich plasma (PRP injections).
- Surgery: Surgery is the last resort for management of sports injuries and is indicated only if conservative techniques are not helpful. Surgeries are performed to repair torn tendons and ligaments or to realign the broken bones. Your surgeon may recommend arthroscopic procedure or open techniques to treat your sports injuries.
Some of the measures that are followed to prevent sports related injuries include:
- Follow an exercise program to strengthen the muscles
- Gradually increase your exercise level and avoid overdoing the exercise
- Ensure that you wear properly-fitted protective gear
- Make sure that you follow warm up and cool down exercises before and after sports activity
- Maintain a healthy diet which will nourish the muscles
- Avoid playing when you are injured or tired. Take a break for some time after playing.
- Learn all the rules of the game you are participating in
- Ensure that you are physically fit to play the sport
