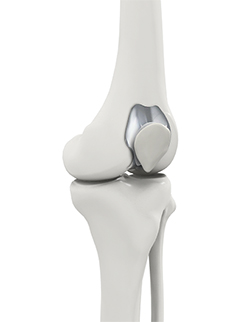
Patello-femoral joint replacement is a procedure to replace the back of the kneecap or patella that is completely damaged. Patello-femoral joint is a compartment of the knee formed by kneecap and femur bone.
The main cause for damage of the patello-femoral component is arthritis, patello-femoral arthritis, where the cartilage wears out causing the ends of the bone to rub against one another. This may cause pain, restrict the movement of knee, and patients may have difficulty in the walking, climbing up and down hill, kneeling, squatting, and standing.
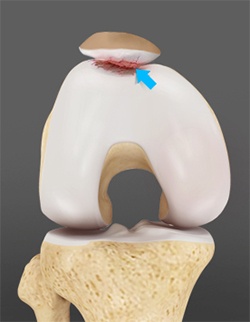
Patello-femoral replacement surgery is performed when pain is not relieved by conservative treatments. Patello-femoral knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery performed by arthroscope. Arthroscope is small fiber-optic instrument having a tiny video camera attached to one end which is connected to a large screen monitor allowing the surgeon to view the knee joint and perform surgery.
Surgical Procedure
- The surgeon makes a small incision, about 3-4 inches long over the knee.
- The patellofemoral compartment is prepared for the artificial components by removing the damaged part of the patella and trochlea, the groove at the end of the femur.
- The new artificial components are fixed in place with the use of bone cement.
- The femoral component is made of polished metal and the patellar component looks like a plastic button which will glide smoothly in a groove located on the femoral component.
- With the new components in place, the knee is taken through a range of movements.
- Once the surgeon is satisfied with the results, the arthroscope and surgical instruments are removed and the incisions covered with a sterile dressing or biologic glue.
Risks and Complications
Post-surgical complications are common with any surgery. The complications associated with patella-femoral replacement include deep vein thrombosis, or blood clots in the leg, infection at the site of surgery, excessive bleeding, injury to the surrounding ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves, and development of a thick fiber around the operated joint which causes stiffness and difficulty in movement.
Post-Operative Care
After the surgery your doctor will suggest pain relieving medications and suggest RICE treatment (Rest, ice, compression, and elevation) which helps to reduce swelling and pain. You will be restricted from physical activity until the knee is healed. Rehabilitation program may also be recommended which involves various strengthening and stretching exercise to control pain and restore the movement of the knee.
Healing may be retarded with use of alcohol, steroids, poor nutrition, diabetes, and smoking, history of heart and kidney diseases, and obesity. Therefore these risk factors should be avoided or controlled to promote faster recovery.
